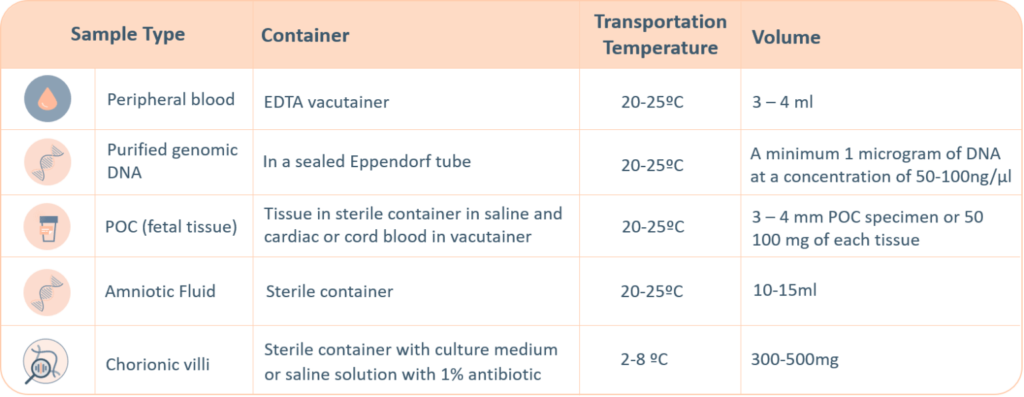
- Chromosomal microarray analysis (CMA), also known as array CGH, is a diagnostic test that can detect clinically significant major chromosomal imbalances (aneuploidies) and sub microscopic (microdeletion / microduplication) copy number variations throughout the genome.
- Chromosomal microarray analysis is the gold standard for the detection of deletions and duplications along the whole genome.
- CMA provides submicroscopic resolution allowing to visualize small regions that karyotyping cannot detect. CMA’s sensitivity relies on the number of the molecular probes used and their genome coverage. The greater the number of probes (180K, 400K, 750K…), the higher their sensitivity.
CMA – Chromosomal Microarray
Chromosomal microarray analysis is the gold standard for the detection of deletions and duplications along the whole genome.